Today in the arsenal of modern dermatocosmetology there is a fairly wide range of methods for the correction of various aesthetic imperfections of the skin - chemical peeling, mechanical skin abrasion, laser coating, microdermabrasion, these contours andare constantly improving.
This trend is particularly typical for hardware methods, especially laser medicine. The use of lasers, first in dermatology and then in cosmetology, has an impressive period. Even more than 25 years have passed since the advent of one of the newest methods of laser treatment - selective photothermolysis. The pioneers of this region, the Americans RR Anderson and JA Parrish, determined the fate of fractional lasers in medicine, making them essential in the treatment of such aesthetic skin imperfections as capillary hemangiomas. Wine port, overgrowth, tattoos, rosacea, pigmentation disorders, photoaging, wrinkles, etc.
Modern skin reshaping techniques
We live in an age where more people are living to old age than ever before. And since many of them continue to live an active life, one of the most important problems in aesthetic medicine is the fight against skin aging.
Plastic surgery can rejuvenate the shape of the face by removing excess skin. However, at the same time, the skin remains variable over time (age-related aging) or external factors (photoaging). It is also important that most patients want to look younger without surgery.
In this case, what method should be used to affect the skin and what should happen to it for its real rejuvenation?
All methods that can be used to improve the appearance of the skin are united by one principle - they use a traumatic effect on the skin, causing fibrosis, which further leads to its intensity and compression.
Currently, dermatocometology uses three main types of skin reshaping, such as:
- chemical stimulation - chemical peels with acids (trichloroacetic, glycolic, etc. ),
- mechanical stimulation - mechanical skin corrosion, microdermabrasion, mesotherapy, fillers, needle subdivision,
- thermal excitation - laser removal, thermal insulation using lasers and broadband light sources, radio frequency amplification, fractional methods.
Chemical stimulation
Historically, acid exfoliation (peeling) was the first method of skin rejuvenation. The principle of peeling is partial (as with superficial peeling) or almost complete (as with medium and deep peeling) destruction of the skin, destructive fibroblasts and skin structures. This damage triggers an inflammatory reaction (the stronger, the greater the volume of the damage itself), which leads to extra collagen production in the skin.However, to achieve the desired result, peeling must sacrifice the skin. Experiments with burns have deceived many, it is said to "prove" that the skin is a self-renewing organ that quickly recovers from the damaged area. In this regard, peeling for a while became more aggressive against the skin (for example, deep phenolic peeling), until eventually the accumulated problems made experts realize the evil spontaneous method that eventually leads to thinning of the skin.
Proponents of deep exfoliation have ignored the emerging problems. Their essence was that due to the destruction of the nipples of the skin and the weakening of the diet, the skin becomes thinner and the number of cells in the layered layer is significantly reduced compared to what it was before peeling. Reducing the barrier function of the stratum corneum leads to a reduction in skin hydration. (Therefore, almost all patients after deep exfoliation for a long time experience severe dryness of the skin) At the same time, the introduction into practice of lighter peels (using trichloroacetic acid and fruit acids) did not meet their hopes for effective skin tightening.Mechanical stimulation
Among the methods of mechanical stimulation of involuntary changes in the skin, dermabrasion using rotary devices (with speed v; rotation of cutters up to 100, 000 rpm) deserves special attention. Currently, modern Schumann-Schreus devices (Germany) are used
The method can only be used in a surgical hospital, as the procedure requires anesthesia, postoperative treatment of the wound surface, a special toilet for the eyes and mouth, as well as feeding devices for patients (due to the fact that the severe postoperative edemaappears 2-3 days after the procedure makes it difficult to open the eyes and mouth).
The method is very effective, but, unfortunately, with mechanical dermabrasion there is a high risk of complications such as:
- persistent postoperative hyperemia,
- the appearance of discoloration areas due to the destruction of melanocytes when the cutter penetrates through the basement membrane;
- wound surface infection,
- scars (if the cutter sinks too deep into the skin)
All of the above have determined the limited application of this method in clinical practice.
Thermal stimulation
Abstract remodeling
Since the late 1980s, a laser has been used to rejuvenate the skin by removing layer-by-layer tissue (removal) [4]. Careful, low-traumatic removal of the surface layer of the skin using a carbon dioxide laser stimulates the synthesis of its own collagen in it, the amount of which increases several times after the procedure. It is then gradually reorganized.
The most effective was the use of CO2 laser, when exposed to a deep thermal effect on all layers of the skin, which is manifested externally by the effect of skin tightening. The method is called "laser dermabrasion", or "laser reappearance", and in terms of effectiveness could not be opposed to any other method of skin rejuvenation that existed at that time (Fig. 1).
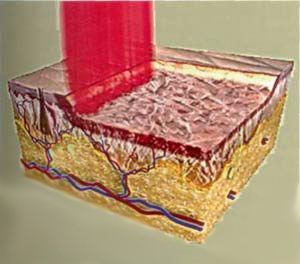
Fig. 1. Design of traditional laser skin rejuvenation (laser dermabrasion)
However, the CO2 laser also causes many complications. In addition, further studies have shown that such a profound effect on the skin stimulates the formation of fibrous tissue to a greater extent than it contributes to the synthesis of a new, physiologically oriented collagen [5]. Developed fibrosis can make the skin look unnaturally soft. The collagen that is synthesized after treatment is absorbed after a few years, just like any collagen is formed at the site of the scar. As a result of thinning of the skin caused by atrophy of the papillary layer of the skin, fine wrinkles begin to appear on the skin. Due to the weakening of the barrier function of the stratum corneum, the level of hydration of the skin decreases and it looks atrophic.
The Erbium-aluminum-yttrium garnet-erbium lasers appeared a little later. Such advantages of an erbium laser as a smaller depth of thermal penetration (erbium lasers penetrate to a depth of 30 μm, CO2 laser - up to 150 μm) and (consequently) the lower risk of burns and tissue carbonation, as well as the relative cost (carbon dioxide), have attracted the attention of many experts around the world.However, as the experience of working with these two types of installations accumulates, the opinion has developed among experts that CO2 lasers are more efficient [6]. Despite the negative effects of carbon dioxide laser skin described above, this method remains essential for correcting acne scars. In addition, it can be considered as an alternative to surgical skin tightening - of all the methods of its remodeling, only CO2 laser exposure can actually cause intense collagen contraction with visible clinical lifting action.
The problem with all the methods described above is that they often "sacrifice", that is, significantly damage the skin. To rejuvenate your skin and look really young, you need a perfect complexion with natural skin nipples, good hydration, normal skin tone and elasticity. The skin is a very complex highly specialized instrument, up to 200 microns thick, which is our only defense against the effects of adverse environmental factors. Therefore, whatever we do to rejuvenate the skin, we must ensure that its underlying normal architecture will not be damaged.
This idea contributed to the emergence of non-abstract skin reshaping technology.
Non-abstract remodeling
The most common devices for non-removable skin reshaping are neodymium (Nd-YAG) and diode lasers, as well as broadband light sources (IPL). The principle of their action - selective photothermolysis - consists in the heating and destruction of structures, which contains a sufficient amount of melanin or oxyhemoglobin. In the skin, these are, respectively, accumulations of melanocytes (lentigo, melasma) and microvessels (telangiectasia). The emitted wavelengths used in non-subtraction lasers correspond to the maxima of the absorption phases of oxyhemoglobin or melanin. The treatment process with non-removable lasers and IPL is quite safe, the recovery period is minimal, however, such a treatment eliminates only the pigment and vascular cosmetic defects. In this case, there is some thickening of the skin, but the result achieved is short-lived.
Fractional skin reshaping techniques
The constant search for new highly effective and at the same time safe methods of skin rejuvenation has led to the emergence of a revolutionary technology - fractional laser radiation delivery. The proposed method of skin rejuvenation has been specially designed to overcome some of the above difficulties. Unlike "conventional" laser abrasive and non-abrasive methods, which are designed to achieve uniform thermal damage to the skin at a certain depth, fractional methods allow to achieve selective microscopic thermal damage in the form of multiple altered columns and leaveareas around these micro-wounds. The industry currently produces two types of fractional lasers: non-abstract and abstract.
The first uses an erbium-labeled optical fiber that produces radiation at 1550 nm. A fractional laser forms thousands and tens of thousands of micro-disorders on the skin in the form of columns - microthermal treatment zones (MLZ) - with a diameter of 70-150 mk to 1359 mcm
As a result, about 15-35 skins are photocopied to the treated area. The chromophore for the laser is water Coagulation occurs mainly in the lower layers of the skin. The stratum corneum remains intact because it contains a relatively small amount of water, and this significantly reduces the risk of infection. The epidermal recovery is rapid due to the low volume of damage and the short migration distance of keratinocytes. The treatment period is accompanied by moderate edema and hyperemia, followed by exfoliation, which occurs on the 5th-7th day. The patient essentially does not lose social activity.This technology - Fractional Photothermolysis (FF) - is a very effective method of non-abstract fractional skin reshaping. To achieve the desired result, a treatment is prescribed. Depending on the clinical condition, it is recommended to perform 3 to 6 procedures with an interval of 4-6 weeks. As with any other non-skin reshaping method, the final result can only be seen 4-8 months after the procedure (cumulative effect).
In cases where a more aggressive effect on the skin is required - for the correction of scars, the removal of deep wrinkles and excess skin, the method of fractional removal (FA or fractional deep skin removal -FDDA) is used.
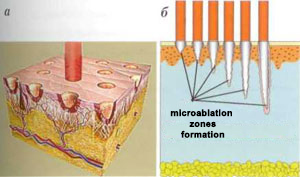
The fractional catalysis method combines the advantages of a CO2 laser with the fractional principle of laser radiation delivery. Unlike traditional CO2 lasers, which remove the entire surface of the skin in layers, FA units form a huge number of micro-deposition bands (MALs) up to 300 μm in diameter at an evaporation depth of 350 to 1800 μm (Fig. 2).
Thus, during this process, the laser radiation, which penetrates into the deep layers of the skin, destroys the upper layer of the skin. In terms of efficiency, abstract fractional laser rejuvenation can be compared to plastic surgery, this is how deep the laser beam is.
Fig. 2. The principle of operation of the abstract fractional laser: the formation of micro-fossil zones - MAZ (a). Dependence of MAZ formation depth on laser radiation power (b)
As in the case of FF, 15 to 35% of the skin in the treated area is actually exposed (in some cases, up to 70%). Recovery after the FA procedure is faster than after layer catalysis. This is because it is an important part of the skin and the stratum corneum remains intact. Bleeding of the skin is observed for some time immediately after the procedure, but soon stops (Fig. 3a, b).
Fig. 3. Step-by-step skin restoration after the fractional removal procedure: view immediately after treatment (a). every other day (b) after 5 days (c) 14 days (d) after a procedure
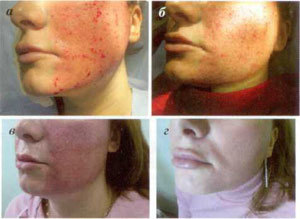
Many small blood cells appear in the skin, which causes a complex cascade of changes that lead to the production of new collagen. Once the bleeding has stopped, it is necessary to remove the serous fluid that remains on the surface of the skin. Its release is observed within 48 hours after the procedure, until the complete epithelialization of the micro-fossil zones takes place. During this period, the patient uses special external wound healing agents. Usually starting from 3-4 days, the peeling and swelling increase (Fig. 3 c). By day 7, these effects gradually subside and erythema remains the only significant side effect (Fig. 3d). The duration of erythema depends on the parameters of the laser exposure and the characteristics of the skin vascularity. According to the author, the erythema lasts no more than 3 months.
The patient's loss of social activity after the FA procedure lasts from 5 to 10 days.
To avoid scars and the appearance of post-inflammatory pigmentation, it is necessary to take care of the skin carefully. Decorative cosmetics can be used from 4-5 days. Prerequisite for a good result is the use for at least 3 months after the procedure of sunscreen cosmetics with a high degree of protection (SPF at least 50). The risk of post-inflammatory pigmentation occurs in 20% of patients and is generally higher in patients with skin phototypes IV-V. This hyperpigmentation is transient in nature and can last from 1 week to 3 months, which also depends on the depth of the treatment and the area of the treatment area. For its prevention 1-2 weeks before the procedure and during another 2 weeks after, external agents based on hydroquinone (4%) and tretinoin (0, 1%) are prescribed. The main effects on the facial skin after the FA procedure are: intense tightening and reduction of excess skin, leveling of wrinkled skin, as well as skin affected by acne scars, reduction of discoloration, porosity.
This method was tried by the author and his colleagues also for removing stretch marks on the skin. As can be seen from clinical studies, the method has been shown to be highly effective in eliminating almost all types of stretch marks, both of which were acquired during adolescence and after childbirth. It was noted that the healing procedures on the skin of the body are different from those on the skin of the face.
Skin reshaping mechanism when using fractional lasers
Let's look at the mechanisms of skin reshaping when using fractional lasers.
After exposure to the laser, aseptic inflammation develops in the area of the formed micro-wounds. The more aggressive the laser exposure, the more intense the inflammatory response, which, in fact, stimulates post-traumatic release of growth factors and infiltration of damaged fibroblast tissue. The impending reaction is automatically accompanied by an explosion of cellular activity, which inevitably leads to the fact that the fibroblasts begin to produce more collagen and elastin. The skin reshaping process involves three classic regenerative phases:
- phase I - alteration (inflammation of tissues). It starts immediately after the damage,
- phase II - proliferation (tissue formation). It starts 3-5 days after the injury and lasts for about 8 weeks.
- phase III - tissue remodeling. Lasts from 8 weeks to 12 months.
After exposure to the fractional catalysis laser, a completely different picture is observed. The trauma caused by this laser breaks the blood vessels and the blood cells, along with the serum, are released into the surrounding tissue. The complete regeneration mechanism of the skin - the alteration of the phase begins - aseptic inflammation develops. Platelets released from damaged blood vessels play an important role in activating blood clotting and releasing chemotoxic agents that, in turn, attract other platelets, leukocytes and fibroblasts. Leukocytes, especially neutrophils, participate in the cleansing of damaged tissue, removing fragments of necrotic tissue, which are partially destroyed by phagocytitis and partially emerge on the surface of the skin in the form of microscopic residues consisting of subcutaneous and subcutaneousnecrotic residues (MENO).
The propagation phase begins in about 5 days. During this period, neutrophils are replaced by monocytes. Monocytes, keratinocytes and fibroblasts continue to influence growth factors and at the same time be under their influence in reverse. Keratinocytes stimulate skin growth and the release of growth factors necessary to stimulate collagen production by fibroblasts. At this stage, new blood vessels are formed and the extracellular matrix is intensively formed.
The last, remedial, therapeutic phase after fractional laser exposure lasts several months.
By day 5 after injury, the fibronectin matrix "fits" along the axis along which the fibroblasts line up and along which collagen will form. An important role in the formation of this matrix is played by the transformation of growth factor β (TGF-β is a potent chemotoxic agent for fibroblasts), as well as other growth factors. The main form of collagen in the early stages of wound healing is type III collagen (this type of collagen is found in the upper layer of the skin, just below the basal layer of the skin). The longer the lesion phase, the more type III collagen will be produced, but in any case, its amount increases to a maximum of 5 to 7 days after damage. Type III collagen is gradually replaced by collagen for about a year Type I, which enhances the strength of the skin. Blood circulation is gradually normalized, the skin becomes smoother and acquires a natural color.Comparative analysis of laser skin reshaping methods
Summarizing the above, here is a chart showing the relationship between the effectiveness and safety of laser skin reshaping techniques.
Advantages of fractional particle rejuvenation methods. Advantages of fractional methods used in clinical practice include:
- Minimal skin damage was checked. Histological studies performed after the procedure show an increase in the number of nipples in the skin, which characterizes the changes in the skin as productive regeneration;
- its effective rejuvenation: the skin becomes thicker, significantly increases the production of collagen and elastin;
- short healing time: average 3 days after FF and 7-14 days after PA,
- minimal risk of overpainting;
- the ability to perform the procedure on patients with thin skin;
- the ability to have a healing effect on any part of the body,
- the possibility of using light types of anesthesia: with fractional photothermolysis, only local anesthesia is used. for fractional removal, a combination of conductivity anesthesia and filtration is required.
- disappearance of telangiectasias (due to the fact that there is rupture of blood vessels in so many places that it is impossible to repair them).
Main indications for fractional therapies
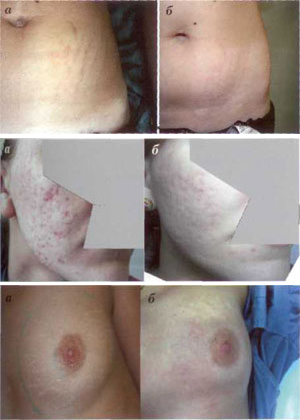
Indications for fractional photothermolysis:
- increase in skin density in the early stages of aging. The FF procedure is relatively easy and can be administered without fear. The therapeutic effect can be exerted on the neck, décolleté, arms, abdomen, thighs, mammary glands.
- photoaging skin,
- hyperpigmentation, melasma,
- hypertrophic scars,
- stretch marks.
Indications for fractional catalysis:
- Wrinkles of varying severity - from fine lines to very intense (in the form of wrinkles);
- age-related loss of skin elasticity and firmness,
- excess skin on eyelids, neck, face (alternative to plastic surgery),
- uneven skin texture,
- intense skin photography,
- acne scars,
- skin deformity after injuries, surgeries,
- hyperpigmentation: melasma, lentinization, stigmatized coloration, etc.
- vascular discoloration,
- skin stretch marks,
- radial keratosis.
In conclusion, a few words about the prospects of using laser technologies in aesthetic medicine. We must pay tribute to manufacturers who have begun to pay more attention to the safety of medical procedures using lasers. Technology is constantly evolving. However, quite often the safety of the method was sacrificed in order to increase its effectiveness. Or vice versa. A compromise was found in a new beginning of the delivery of laser radiation to the tissue. It should be noted that the types of lasers remained the same: erbium, carbon dioxide, neodymium. This indicates that:
- First, laser skin reshaping is recognized as the most effective today.
- second, the coverage of aesthetic and dermatological problems solved by these methods is extremely large - from skin rejuvenation to the treatment of congenital and acquired skin pathologies;
- third, with the advent of fractional technologies, the safety and effectiveness of treatment have become predictable.














































































